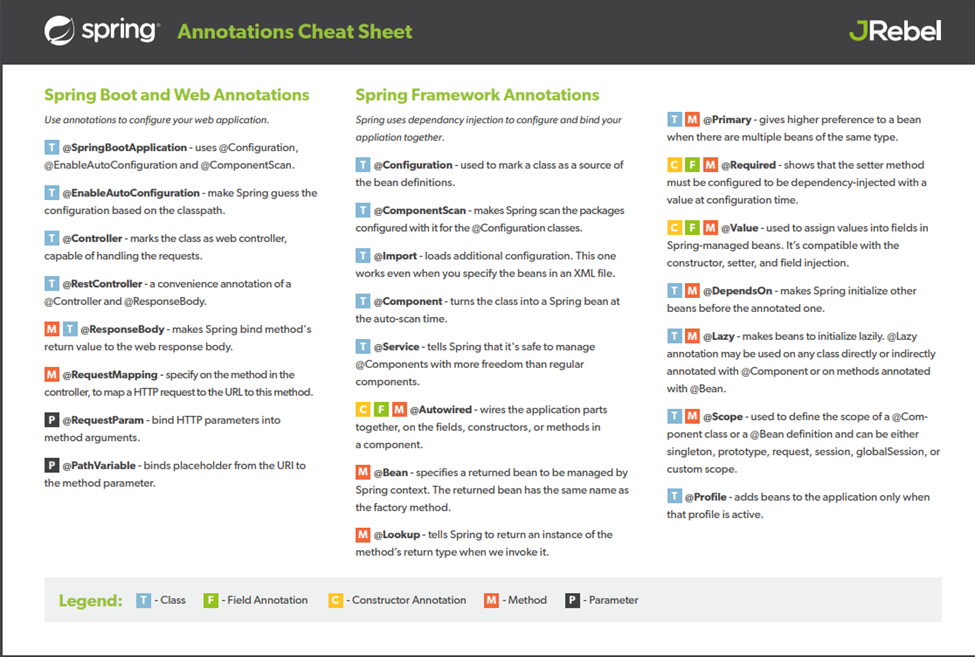
Spring boot handy code
Spring Boot Handy Code
Notes from
infybuzz tutorial
1.
Spring Cloud
-
It is providing projects to quickly create micro
services
-
Official website, https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud
2.
We learning following Spring cloud projects
-
Spring
cloud web client (this will help in communicating between 2-different micro
services without rest template in a programmatic way, for more details click
here)
-
Spring
cloud open feign (this will help in communicating between 2-different micro
services without rest template in declarative way, for more details click
here)
-
Spring
cloud netfilx Eureka (this is service discover and registry server for all
our running micro services, for more details click here)
-
Spring
cloud load balancer (this will balanced the load, for more details click here)
-
Spring
cloud API Gateway (this will be the main entrance like authorization and
many more, for more details click here)
-
Fault
Tolerance, Circuit Breaker (this will handle the failure of micro services,
for more details click here)
-
Sleuth
and Zipkin (this will help in tracing down the services, Zipkin is the UI
tool for tracing down, for more details click here)
-
Config
Server (common properties will be store and common repository, for more
details click here)
Terminology:-
Microservice – one single application for e.g.,
studentmicroservice, addressmicroservice etc
RestAPI – it’s an API (service) in application for e.g.,
/createStudent, /getStudents etc
Swagger
Add maven dependency
Then in browser, hit url
http://localhost:9090/swagger-ui/index.html
or http://localhost:9090/swagger-ui.html
If swagger url don’t work just rebuild the project.
Communication
between different micro services: -
To call RestAPI from different micro services we use “RestTemplate” but from Spring 5, Rest template is deprecated
and now, we are using spring cloud “webClient” and spring cloud “openFeign”
To understand web-client concept, we are using student micro service (SMS) and address micro service (AMS), we are calling RestAPI’s of AMS from SMS
Web
Client provides programmatic way to call RestAPI from other micro services.
1. Add “webflux” dependency in calling micro service as shown below:
1.
Create a WebClient
bean in student micro service by providing address micro service url as
shown below:
1.
Create a method to call required RestAPI from
address micro service, as shown below:
Spring cloud open feign:
Spring cloud open feign provide
declarative way of calling RestAPI from other micro services. Feign client is
an interface
Steps to use open feign
1.
Then create a package where you will be storing
all feignClients interfaces in your project
1.
Then add “@EnableFiegnClients” annotation in
main class pointing to the folder containing all feign clients
1.
Create an interface in fiegnClients package and
configure url, path, value and properties accordingly then copy the
required RESTAPI, method signature from the called micro service as shown below
Summary of Spring Cloud Open Feign-
- Add dependency “spring-cloud-starter-openfeign” in calling micro-services
- Create a package to store all feign clients
- Add “@EnableFiegnClients(pointing to feign client package address)” in main class of micro-services
- Create an feign client interface as shown above and call interface method as required, and the implementation of those methods are in called micro-service
Spring cloud netfilx Eureka
Service Discovery and
registry is helpful in managing micro-services, each micro service will
register itself with Eureka server and while communicating between
micro-services we will be using service name(application name) instead of micro-service
url.
FYR, before using Eureka server, in application properties of
both Student and Address micro service we used application name
Student Micro-service properties file, we are calling url of address
micro-service
In addition, add following properties into eureka-server
In addition, add @EnableEurekaServer annotation in Eureka-server
application main class as shown below
Now, we have to add “eureka-client” dependency in student and address
micro-services or all other services who wants to register themselves with
eureka servers
Then add @EnableEurekaClient annotation
in micro-services as shown below
Then add below config property in micro-service properties file
In above instances currently registered section
Eureka also registered itself, to avoid we have to set below property and in
subsequent screenshot you can see that Eureka is not registered.
Once you registered all your micro-services with Eureka
server, to communicate between micro-services via feign-client, we will be
using service name registered in Eureka.
Summary of Eureka
Server:-
- Create an application with “Netflix-eureka-server”
- Give port and application name in property file and add @EnableEurekaServer annotation on main class.
- Eureka server is ready.
- To register micro-services into Eureka server inject “netfix-eureka-client” dependency and add @EnableEurekaClient annotation in main classes of all micro-services
- Add “eureka.client.service-url.defaultZone=http://localhost:8761/eureka” property in all micro-services, to register themselves into eureka.
- To avoid eureka to register itself into eureka add following properties into Eureka Server application
Spring cloud load balancer
Student micro service is calling services (RESTAPI) from
address service using feign client. To manage load of address service in
student service, we will be configuring client-side load balancer in student service in next
steps.
Add below dependency in student service
Then create load balancer configuration file for the
required feign client interface, here we have “address-feign-client” so
we will be creating load balancer configuration file for the same as below.
@LoadBalancerClient(value = "address-service")
public class AddressServiceLoadBalancerConfig {
@LoadBalanced
@Bean
public Feign.Builder feignBuilder(){
return Feign.builder();
}
}
Spring Cloud API-gateway:-
Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective
way to route to APIs and provide cross cutting concerns to them such as:
security, monitoring/metrics, and resiliency. Previously we use “Zuul”
project but from spring 5, it has been deprecated.
Once we implement API
gateway then we will give API gateway url to consumer, once user access any API
from student or address micro services,
API gateway search for service name in eureka server and navigate to the
requested URL.
Therefore, after implement API-gateway URL will be changed
as shown below:
API-gateway url – http://localhost:9090
Student service – http://localhost:9091
Address service – http://localhost:9092
From: - http://localhost:9092/api/address/getAddresses
To: - http://localhost:9090/address-service/api/address/getAddresses
From: - http://localhost:9091/getAllStudents
To: - http://localhost:9090/student-service/getAllStudents
Address-service
and student-service
are the application name given in properties file
1.
We have to create a project with “api-gateway”
dependency; this project will work closely with Eureka server so we have to add
“eureka-discovery-client”
dependency as well.
2.
Add “@EnableEurekaClient” annotation in main class and add
below properties in api-gateway project
Pre-Filter:
-
Pre-filter is executed before our micro-service is called,
and it is executed in API-gateway as shown below
Just we have to create a bean annotated with “@Configuration”,
implements “GlobalFilter” and implements method. In above image all the
highlighted lines before “return statement” is execute before
calling API, those lines are refer as pre-filter.
Post-Filter: - Post-filter is executed after our micro service is called,
Spring Cloud
open-feign with API-gateway:-
To implement open-feign with API-gateway we have to make slight
modification in open-feign class as shown below
Points to remember:
1.
if we create feign-client interface with “api-gateway” as
shown above then it is common feign-client, means we can call any micro service
from this feign client by passing complete path as shown in above pic
2.
If we create, as above then “api-gateway”
will handle load balancer among instances, we do not have to create separate
load balancer as we created before (Address Load balancer config).
Fault Tolerance, Circuit breaker
with Resilience4j: -
In above example, student-service
is calling address-service and it is down, due to which student-service will
also observe more failures and rest all micro-services will also observe the
same. To avoid such failures we will be implementing fault-tolerance using Resilience4j.
From above pic, student-service is
calling address-service, if everything is fine in address-service then switched
is closed else switch will open, we have to handle this circuit breaker in our
micro-services using switch concept.
Circuit breaker states: -
Closed – all calls are allowed from student-service to
address-service.
Open – no calls are allowed from student-service to
address-service.
Half Open – few calls are allowed from student-service to
address-service.
Circuit breaker properties: -
Points to remember:
-
1.
slidingWindowSize - is a numeric value that has to be set, it will check the last
number of calls.
2.
failureRateThreshold – it has to be
set in percentage
3.
Failure Rate – it is the number of
failed request, if failure rate is greater than the threshold then switch will
be open, and give time to micro-service to resolve issue.
4.
waitDurationInOpenState – it will be
open state for time specified then it goes to half-open state after specified
time, as we can’t keep the switch opened for long time.
5.
permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState – again
it will check the condition and decide whether to open or closed
switch.
Implementing Circuit Breaker using Resilience4J: -
1.
add “resilience4j-spring-boot2”
and spring-aop dependency in calling RestAPI, here
it is student micro-service
1. add following properties in calling RestAPI, here it is student micro-service
1. to work fault tolerance, create a service and add all the methods which are using feign-client, so that spring AOP will work as expected, for that we have created a bean as below,
Add “@circuitBreaker” annotation with same
name parameter used in properties file “addressService” as shown above to
the method you wanted to handle fault tolerance.
1.
“@CircuitBreaker (name = “<service
name>”, fallbackMethod=<should have
same method signature>) and fallback method is mandatory to handle
fault tolerance.
2.
Earlier spring was providing “Spring Cloud Hystrix” but now it is
deprecated and “Resilience4j” is
being used.
Notes from
in28Minutes on Resilience4j:
In below code @Retry, @CircuitBreaker annotations are coming from resilience4j library.
Generally, @Retry(name =”default”), which means it will retry for 3-times then it will throw exception, if you want to configure by your side then give the name as required and configured the same in application.properties
In above “sample-api” is
user define name and you can change default
to any userdefine name
@CircuitBreaker is the advance version of @Retry. @Retry will always hit the url even the microservices is down whereas @CircuitBreaker follow hit only after time specified. For more details on CircuitBreaker check above notes
Sleuth
and Zipkin: -
Sleuth will help
developers to identify which service is down by adding unique format {service-name,
traceId, spanId} in log
statements, in below example T-1 is
trace Id which is common across all micro-services and S-1, S-2, S-3 are the span Id with is unique in a service.
Zipkin will help
to monitor sleuth in a graphical way
Steps: -
1.
We have to add “spring-cloud-starter-sleuth” dependency
in all micro-services except Eureka
2.
Add sleuth configuration property only in “API-Gateway”
application properties
3.
Add log statements in required RestAPI.
In application.properties file of API-Gateway
Output: Log
statements from student-service and api-gateway
Zipkin: -
zipkin is a UI tool/server, which shows the graphical representations of API
calls and show the complete flow of API.
1.
Download and execute zipkin executable jar from https://zipkin.io/pages/quickstart.html
1. To
register your micro-service with zipkin add below dependency “spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin”
1.
In addition, add zipkin configuration property in
all your micro-services
Now, hit url - http://localhost:9411/
And Enjoy J
Note: - in API-gateway micro-service, do not add version
tag in sleuth and zipkin dependency
Cloud
Config Server: -
It helps to centralize all applications properties in a
centralized repository (like git/svn), so that if there’s any change in
properties, we do not need to deploy the whole application just refresh application-using
actuator API.
Steps: -
1.
Create a local git repository and copy all
micro-services properties files by renaming them as micro-service name <application-name>.properties
1.
Remove spring.application.name=address-service from all
properties file stored in local repo.
2.
Now, create new application namely “cloud-config”
with “spring-cloud-config-server” dependency and to register
cloud-config application into Eureka server then add “eureka-client” dependency
also. In addition, add @EnableConfigServer, @EnableEurekaClient on main class.
3. In cloud-config property file, add below lines
In above pic server.git.uri is pointing to local git
repository containing all micro-services properties files.
Sometimes you will get error like noSuchLabelFound
in console, it because our application is failed to connect git repo,
to avoid the error execute cmd: git branch then you will get
result “* master” or something like this, take the name after * and add below property in cloud-config-property file
spring.cloud.config.server.git.default-label=master
Hint: - copy the folder path and open in
browser, you will get uri then copy path, shown below
1. Add “spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap” and spring-boot-starter-actuator dependency in all micro-services and rename the property file to “bootstrap.properties” as shown-below and keep only few configuration properties into it
spring.cloud.config.discovery.enabled=true – it will
enable to discover/look for micro-services in Eureka
Spring.cloud.config.discovery.service-id = config-server –
it will search for the provided service-id/ service-name in Eureka, here it
will search for config-server
spring.cloud.config.profile=dev it will use the provided
profile from local repository. As our local repository will have to properties
with different profiles like dev, prod etc. with the help of the config we can
force micro-services to use respective profile. Here we are using “dev”
profile
spring-boot-starter-actuator – dependency
will help micro-services to refresh/pick-up changes from local repository property
files instead of deploying the whole application. To achieve this follow below
steps:
1.
Add spring-boot-starter-actuator dependency in micro-services
2.
Add in property file, management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=* it
will help micro-services to pick-up/refresh changes from local repository properties
files instead of re-deploying whole micro-services.
3.
Add @RefreshScope annotation on
Bean/Class/Services places to refresh value, note- this annotation will not
work on Controller class and any singleton scope beans
4.
Run http://localhost:9090/address-service/actuator/refresh
as below, it will show all changed properties and from then it will force
micro-services to use the updated profile.
Notes from in28Minutes Master in spring boot and spring cloud
Spring boot and
spring cloud notes
1. REST
– Representational State Transfer, they use proper use of HTTP/HTTPS
2. GET,
PUT, POST, DELETE are the HTTP request methods and 200, 404.. are the HTTP
status codes of response
3. REST
API contains request header, request body and response
4. A
resource has an URI(uniform resource identity) e.g., /users/todo,
/users/createuser, /users/getuser/1
5. In
REST data exchange can be done in xml, json and other formats, REST is
architectural approach.
6. SOAP
uses wsdl, SOAP – simple object access protocol. We use xml for exchange
request and response
7. Spring web – build web, including
RESTful, applications using Spring MVC, uses apache tomcat as default server
8. Spring boot devTools – provide fast
application restarts, LiveReload and configurations for enhanced development
experience
9. Spring data jpa – persist data in sql
stores with java persistence API using spring data
1. Spring boot Auto configuration – it
configures the dependency found in class path, to know more about it run
application by adding “logging.level.org.springframework = debug” in
properties file and check “Auto-configuration Report” in
console.
2. Dispatcher Servlet – “/” it is the root
of the web application, all the request followed by “/” is handled by
dispatcher servlet.
3. “@RestController”
– check the docs of it, it is responsible to convert the response into JSON
format.
4. @AutoWired
– it is used for dependency injection, all loaded beans are eligible
for auto wiring to another bean Here, we can see two types @Autowired by name
and @Autowired by type. Even how to use @Autowired in properties, @Autowired in
setter methods, @Autowired in constructor, @Autowired in @bean in spring boot.
@Autowired by Type in Spring boot
The @autowired annotation is used to inject
dependency. Dependency injection is done in two ways, by name and by type.
@Autowired by type uses the class type to auto wire the spring boot bean class.
The bean class can be auto-wired with the class name. Only one bean class
should be loaded into the ApplicationContext.
@Componentpublic class Car { }
@Componentpublic class VehicleService { @Autowired Car myCar;}
@Autowired by Name in Spring boot
The @Autowired annotation is used to inject a bean in another
class in two ways. One way is @Autowired by name. For auto wiring by name, the
name of the variable is used for the dependency injection. The name of the
variable should be the same as the name of the class or the bean name
configured in the @Component annotation.
@Component
public
class VehicleService {
@Autowired
Vehicle car;
}
@Component
public
class Car implements Vehicle{
}
public
interface Vehicle {
@Autowired in properties
The @Autowired annotation injects a bean class configured as the
properties of another bean. Properties in a class are automatically assigned
with a value or a reference of another class. It avoids the explicit call of
getter and setter methods. The @Autowired annotation in properties is used to
initialize variables in the class.
@Componentpublic class VehicleService { @Autowired Vehicle car; // ---> By name @Autowired Car mycar; // --> By type}
@Componentpublic class Car implements Vehicle{} public interface Vehicle {}
1. 1. get HttpStatus codes
2.
@controllerAdvice – if we want one
controller to be applicable across all others controller we will use this
annotation. helps in Exception handler. Check docs for more details,
3.
@Valid
– it will be added to request body or variable, if validations fail it will
trigger handleMehtodArgumentNotValid() from ResponseEntityExceptionHandler.class..
all this validation is available in java validation API , spring boot starter
web provide all this validation by default,
4.
HATEOAS
– it will be helpful in adding links to response data. First add HateOAS
dependency and response type of method should be either EntityModel or CollectionModel
then create link and add to response as shown below:
- First we have to create properties file inside ResourceBundle
folder (it is optional); property file name should start with “messages”
exactly as “messages”, “messages_fr”, “messages_nl” etc.
- Then Autowired below component
- In above code “good.morning.message” is the property define in resource
bundles
2.
Actuator - In
essence, Actuator brings production-ready features to our application. Monitoring
our app, gathering metrics, understanding traffic or the state of our database
become trivial with this dependency. Actuator is mainly used to expose
operational information about the running application — health,
metrics, info, dump, env, etc. It uses HTTP endpoints or JMX beans to enable us
to interact with it.
-
Endpoints:
default endpoint <url>/actuator,
some of the endpoints are /health, /beans, /shutdown,
/threaddump etc..
-
To access Actuator endpoints, add dependency
and a property management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
- Visualizing
API’s with HAL explorer: HAL stands for JSON Hypertext Application Language, is a simple format that gives
a consistent and easy way to hyperlink between resources in our API.
Including HAL within our REST API makes it much more explorable to users
as well as being essentially self-documenting. HAL explorer helps you to
explore the API in a declarative and easy way.
Add dependency - spring-data-rest-hal-explorer and run application on root url
http://localhost:1991/
1. Filtering Response – Hiding some of the
field from API response is called filtering, to achieve it we have 2-options
Generic sample of someBean
- Static : In Static, to hide a field we will be using “@JsonIgnore” annotation on field as shown below
Or you can use “@JsonIgnoreProperties” annotation on class as shown below
So
from all responses hardcoded fields will be hidden. To hide some field1 in one
response and field2 in another response we have to use dynamic filtering.
-
Dynamic :
In Dynamic, we will hide different fields as required. To achieve it we
have to remove all “JsonIgnore” annotations from response body and add “@JsonFilter(<filterName>)”
on response body, return type of the API should be “MappingJacksonValue”
In Response Body:
In API:
1. How to create 2-different Version of same
service (API) –
There are multiple ways of doing the same
thing,
- By using Request Param, see below for your reference.
url will be
- http://localhost:1991/person/param?version=1 and http://localhost:1991/person/param?version=2
-
By using
headers, it is called header versioning; see below for your reference.
url will be same – http://localhost:1991/person/header
for both, with this you have to pass in headers key-value in postman as shown below
url will be same – http://localhost:1991/person/header
for both, with this you have to pass in headers key-value in postman as shown below
Types of
versioning and their usage shown in below pic:
1. To
use *.sql scripting file or any sql scripting file from application, we have to
add following property into application.properties file
spring.jpa.defer-datasource-initialization=true
Spring
Cloud :
Spring
Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common
patterns in distributed systems (e.g. configuration management, service
discovery, circuit breakers, intelligent routing, micro-proxy, control bus,
one-time tokens, global locks, leadership election, distributed sessions,
cluster state). Coordination of distributed systems leads to boiler plate
patterns, and using Spring Cloud developers can quickly stand up services and
applications that implement those patterns. They will work well in any
distributed environment, including the developer’s own laptop, bare metal data
centres, and managed platforms such as Cloud Foundry.
Spring cloud is not just a single project it contains
multiple projects like eureka server, spring cloud config server, spring cloud
api-gateway etc that make developer life easy
There are many release of spring cloud like finchley M2, EdgwareM1,
Brixton and Angel SR6
|
Challenges in microservices |
Solution from Spring Cloud |
|
Configuration management |
Spring Cloud config server |
|
Dynamic scale up and down
microservices |
Eureka, load balancer |
|
Communication between
microservices |
Feign Client |
|
Visibility and monitoring |
Sleuth - Zipkin, API-gateway |
|
Fault Tolerance |
Circuit breaker, Resilience4j |
|
Application |
Port |
|
Limits Service |
8080, 8081, ... |
|
Spring Cloud Config
Server |
8888 |
|
Currency Exchange
Service |
8000, 8001, 8002, .. |
|
Currency Conversion
Service |
8100, 8101, 8102,
... |
|
Netflix Eureka
Naming Server |
8761 |
|
Netflix Zuul API
Gateway Server |
8765 |
|
Zipkin Distributed
Tracing Server |
9411 |
Spring Cloud Notes
1.
if you add cloud config dependency in your
pom.xml i.e., spring-cloud-starter-config
Then you have to define config server
connection details into application.properties
spring.config.import=optional:configserver:http://localhost:8888
“If you have not created config server so far then you have to add [optional]”
1. There
are 2-ways to use properties values define in application.properties file in
our controller/service layer
-
By using “@value” annotation over a variable
declared, FYI
-
By creating configuration class annotated with “@ConfigurationProperties(<name>)”
Variables
declared in configuration file i.e., minimum and maximum will match the
value in property file. See highlighted parts for your reference.
To get more details visit: https://www.baeldung.com/spring-value-annotation
1.
To get the port in our bean we can use
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
environment.getProperty("local.server.port");
Implement
Notes on Microservices challenges and solutions from github
Implement
Notes on Exception handler
Microservices
with Docker
Cmd-1:
docker run
in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE -or- execute below
docker run –p 5000:5000
in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE
hub.docker.com is contains
repositories concept is same like github
Image
– it is static template, on repository it is a set of bytes even after
downloading to your local machine it is just a set of bytes
Official
image - The Docker Official Images are a curated set of Docker repositories
hosted on Docker Hub. Docker, Inc. sponsors a dedicated team that
is responsible for reviewing and publishing all content in the Docker Official
Images. This team works in collaboration with upstream software maintainers,
security experts, and the broader Docker community. Like plsql etc
Container
– running version of image is called container, we can have multiple
container for the same image.
Cmd-2 : docker
run –p 5000:5000 -d in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE ; -d refers to
detach mode which means container will run in background without generating
logs. To see logs execute
Above command download image only once,
later it will use it from local machine
FYI, docker run command is nothing but
docker container run
cmd-1:
docker run –p 5000:5000 -d
in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE ; -d refers to detach mode which means container will run in
background without generating logs. To see logs execute
some sample run options : -
docker run –p 5000:5000 -d
in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE ; here we are running application in detached mode
docker run –p 5000:5000 –m 512m –cpu-quota 5000 -d in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE; here we are assigning resource of 512mb of
memory and 5% of cpu quota
Above
command download image only once, later it will use it from local machine
FYI,
docker run command is nothing but docker container run
cmd-2:
docker stats ; it will give the statistics of running containers
cmd-3:
docker system df ;
cmd-4:
docker logs <containerId of the image;
first few characters of string is also fine>
cmd-5:
docker container ls [-options] ; it will list all the container status
cmd-6:
docker run –p 5001:5001 -d
in28min/todo-rest-api-h2:1.0.0.RELEASE; it will create the container of
same image on different port. Here It is 5001
cmd-7:
docker images ; shows the images
downloaded into our local machine
cmd-8:
docker stop <container id> ; it
will gracefully shutdown container
cmd-9:
docker kill <containerId>; it
will stop container immediately
cmd-10:
docker pull <official/user added
image> ; it will download image to our local machine; Eg., docker
pull mySql, docker pull <software name> etc.
cmd-11:
docker image history <image id>
cmd-12:
docker image inspect <image id>
cmd-13:
docker image remove <image id>; it
will remove image from local machine only
Docker
Architecture
Docker Client: place where we
are executing the commands
Docker Daemon: it is
responsible to run containers and manage images locally, create images, pushing
images into registry
Why
Docker is popular:
Before Docker we have Virtual Machines
**********Alhamdulillah**************

























































Comments
Post a Comment