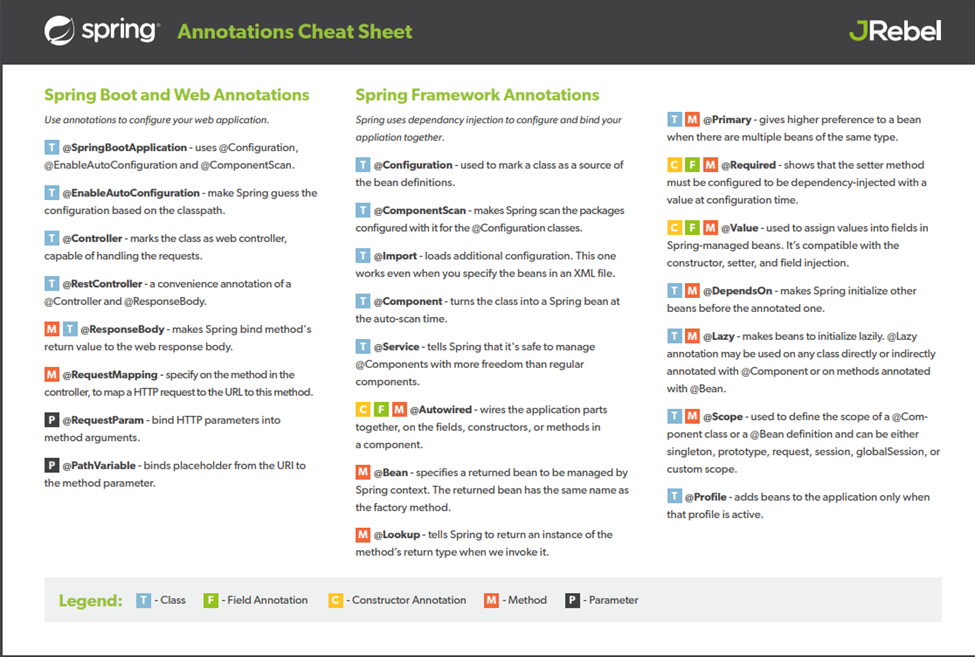
Git-hub handy code
.git/Github handy code
Points to Remember:-
1.
git is a
versioning tool to keep track of changes and collaboration with team.
2.
We install git
in our local machine to connect with github on internet and push our code
for versioning to local and remote locations.
3.
On github we will
create repositories, branches, masters etc for versioning.
4.
In this handy
code, we will be learning git and it’s command and structure.
6. Download and install git.exe file from website - www.git-for-windows.github.io
7. To verify git installation execute “git version” in command prompt, it will give you the installed version.
After
installing git tool, we have to set configuration for reference,
git config --global user.name = “pasha”
git config --global
user.email = “mdjahangirpasha.adf@gmail.com”
When you want to check the global config details,
execute below command
git config --global --list
8. Git workflow
9.
We can versioning
an empty folder or an existing project locally.
10.
Now, we are
trying to version an empty folder and add some files into it, whenever we
version any folder there will hidden “.git” file will be created, its means
that the folder is ready for version control.
→ we have created an empty
folder namely “git-handy-code-ref”, navigate to folder location
in command prompt and execute command “git
init”then “.git” file
will be created.
→ else you can execute “git init <folder name> then it
will create a folder as name specified with hidden “.git” folder.
→ to make an existing
project(angular, spring boot projects) to be versioned just navigate to the
project base folder and execute command “git
init” then the folder and all of it’s files will be added to git
working directory, then to add those files to local staging area execute “git add .”
11.
Now, we will add
some file, README.md into the folder
in above pics we have 2-files “README.md”
is modified and “firstfile.html” as added and we execute “git add .” command to add all newly
added files and modified files to local staging with just single command.
Now, we have to commit all our clean code into local git repository
to commit changes execute git commit -m “initial commit”
we can combined multiple git
commands, for example to add and commit at same time we can use git commit -am "nice message"
List of git commands
1. Git initialization
git init [project-name]
project-name parameter is
optional. If not supplied, Git will initialize the current directory.
2. Git Add
git add file-name
Adds the new or newly modified file-name
to Git's staging area (index).
3. Adding All Changed
Files
git add .
The period parameter for the git add command will recursively
add all new and newly modified files.
4. Git Status
git status
Shows, which files have been, modified in the working
directory vs Git's staging area.
5. Git Commit
git commit -m "A really good
commit message"
Commits all files currently in Git's staging area. The -m
parameter allows for a commit message directly from the command line.
6. Express Commit for
Tracked files
git commit -am "Awesome commit
message"
Use the -a parameter with the git commit command to directly commit newly
modified tracked files. Warning: Only do
this for small changes. Tracked files are files that have been previously added
to Git (committed or staged).
git reset HEAD file-name
Following the above command will "unstage" the
specified file from Git's staging area (aka index).
8. Backout Working
Directory Changes
git checkout -- file-name
Following the above command will back out any changes made to
the specified file and replace it with the version last committed in Git
9. Seeing Repository
History
git log
git help log
git log --oneline --graph --decorate
--color
Git's log command displays
the repository's history in reverse chronological order. The no-params version
displays the standard view.
Git log options from above: --on-line Compacts log data on to
one line, abbreviating the SHA1 hash --graph Adds asterisk marks and pipes next
to each commit to show the branching graph lines --decorate Adds the markers
for branch names and tags next to corresponding commits --color Adds some color
to the output -- nice to have, depending on the operating system
10. Removing a file
using Git
git rm file-name
11. Removing a file
using Terminal
rm file-name
This removes the file outside Git's knowledge
12. Updating Git's
Index (staging area)
git add -u
The -u parameter will
recursively update Git's staging area regarding deleted/moved files outside of
Git.









Comments
Post a Comment